Methylation Detection - MS-HRM Technology
Methylation testing of HRM technology services (MS-HRM technology)
DNA methylation is a covalent modification that occurs on DNA base sequences. In mammals, DNA methylation occurs primarily on the cytosine of the 5'-CpG-3' dinucleotide sequence. In the human genome, approximately 60% to 70% of CpG cytosines are methylated, the extent of which varies with species and cell types. The DNA methylation status exhibits a certain distribution pattern in the genome, and 90% of methylcytosine is located on the repeat sequence. DNA methylation can be inherited and alters the structural properties of DNA and how it behaves.
DNA methylation significance:
The presence of a methyl group on the target sequence can affect the binding of the transcription factor, causing transcriptional repression, thereby inhibiting expression of the gene. Methylation of the promoter region CPG island can often inhibit the transcription of the gene, especially for tumor suppressor genes, apoptosis-related genes, DNA repair genes, etc., methylation of the promoter region will affect the function. Different tumor tissues have different methylation status and can be used as an early marker to monitor tumor formation. For the methylation of certain specific genes, it is more important, such as DNA repair genes, which can cause sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs, and thus serve as an evaluation index for the therapeutic effect of drugs, and guide clinical drugs.
Detection method:
Methylation-specific PCR, Northern blotting, Western blotting, immunocytochemistry, etc. These assays require a lot of time and cost, and have certain difficulties in clinical application.
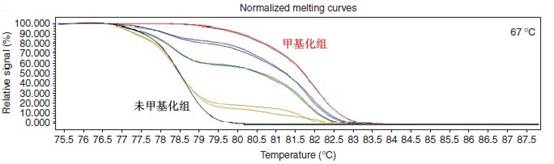
High Resolution Melt (HRM) is a new technology for detecting CpG sites in epigenetics, based on DNA sequence length, GC content, base complementarity differences and specificity. Saturated dyes can be inserted into the double strands of DNA, and high-resolution melting curves can be used to analyze the samples, and the resolution can be distinguished from single base differences.
As a new generation of genetic scanning tools, HRM has the advantage that other technologies such as “ simple, efficient, fast, and inexpensive †are incomparable:
Jane: no sequence-specific probes, no base sites, simultaneous detection of known or unknown mutations, SNPs and methylation sites; closed-tube operations to avoid cross-contamination.
Efficacy: The minimum detection of 0.1%-0.01% of mutation or abnormal methylation, detection of SNP sensitivity and specificity are 100%.
Fast: No more than 384 samples are detected at the same time, and the test is completed within 60-90 minutes.
Integrity: Simplify the operation steps, reduce labor and reagent costs, and cost far less than sequencing, Taqman probes and other methods.
HRM technology is especially suitable for SNP, mutation or methylation analysis with large sample size and few detection sites. It is a high-throughput method different from gene chip detection method (more detection sites and fewer samples). At the same time, it is also the best way to verify multiple genes after gene chip screening in more samples.
DNA methylation-HRM detection principle:
   MS-High Resolution Melting Curve Analyse is a simple and sensitive method for detecting the methylation level of a gene without the subsequent manipulation of the PCR product. This method is mainly achieved by comparing the melting temperature and peak shape of the curve and can detect the occurrence of a single methylation in some columns of CpG sites, and can also methylate a series of CpG sites. Analyze horizontally. The methylation and average methylation levels of a single CpG site affect the shape of the melting curve. Treatment of the DNA template with bisulfite can convert 5-methylcytosine to uracil. Prior to the PCR reaction, a pair of primers for the sodium bisulfite-treated DNA strand were designed at the non-CpG island site, which contained meaningful methylated CpG islands in the middle of the primers. Once these CpG islands were methylated, Cytosine (C) does not change, and unmethylated cytosine (C) is converted to thymine (T), the GC content in the sample changes, and finally converted to the melting curve Tm value difference. The relative position of the CpG site within the small amplified fragment also affects the shape of the melting peak. Therefore, the methylation site and methylation level of the sample can be detected based on the Tm value and the shape of the melting peak.
The HRM method is more convenient, sensitive, reproducible, low cost, and not limited by the detection site. It will provide more help for research and clinical applications in genetics and oncology.
Guava White Tea,White Tea Leaves,White Peach Tea,Silver Needle White Tea
Hunan Junshan Yinzhen Tea Industry Co.,Ltd , https://www.junshan-tea.com