Straw feed primarily refers to the stalks of leguminous crops and the straw from grasses. Grass crop stalks include corn stalks, wheat straw, rice straw, while legume crop stalks consist of soybean, broad bean, and other vine residues. These materials are widely used as livestock feed, especially for sheep.
The nutritional profile of straw feed is characterized by a high fiber content, typically ranging from 30% to 40% of dry matter. It also contains significant amounts of lignin, hemicellulose, and silica, which form a tight bond with cellulose, making it difficult for animals to digest. The rough texture further reduces its palatability. On average, the energy value of straw feed ranges between 7.78 MJ and 10.4 MJ per kilogram. Crude protein levels are low, with legume straws containing around 8.9%-9.6%, and grass straws about 4.2%-6.3%. Fat content is generally below 1.3% to 1.8%. Mineral content is also limited, lacking essential elements like zinc, copper, sulfur, selenium, and iodine, as well as lower calcium and phosphorus levels than what sheep require. Additionally, vitamin A, D, and E are often deficient, which can impact growth and health in sheep.
Despite these shortcomings, straw can be significantly improved through various treatments such as silage, ammoniation, or fermentation, enhancing both its nutritional value and taste. This makes it a cost-effective and widely used feed source during the winter months.
Various feeding methods have been tested to improve the performance of sheep on straw-based diets. For example, using silage corn stalks combined with concentrate feed and mineral additives resulted in an average daily weight gain of 135 grams and a monthly gain of up to 6.7 kilograms. Ammoniated wheat straw increased feed intake by 41% compared to traditional dry straw, leading to higher weight gains and better economic returns. Similarly, hot-jet treated wheat straw improved daily weight gains and feed efficiency, showing promising results.
In another study, micro-fermented corn stalks significantly boosted weight gain in lambs, with a 67.3% improvement over untreated straw. EM-fermented straw also showed positive effects, with a 12% increase in daily weight gain when used as an additive. These findings highlight the importance of proper treatment in maximizing the benefits of straw feed.
To get the best results, it’s important to balance the diet by adding some concentrate feed—ideally at least 10% of the total ration. Non-protein nitrogen sources like urea (3%-5%) can also enhance digestibility. Including essential minerals and vitamins ensures a balanced diet, supporting optimal growth and productivity in sheep. With proper management and processing, straw remains a valuable resource for sustainable livestock farming.
Fiberglass Grating
Fiberglass Grating
The fiberglass grating also named FRP grating & fiberglass grid, and the fiberglass grating panels can be made into FRP grating cover, fiberglass walkway grating, fiberglass trench grating and so on.
The fiberglass grating is light in weight and has good elasticity, so it can be cut freely during the installation process, without using lifting equipment, and only a small amount of labor and cutting tools are required. Because the FRP grid is made of non-metallic materials, the corrosion resistance of the FRP grid is very good. The FRP grid will not rust and rust under the chemical medium, nor will it damage the structure of the material.
Beyond that, the color of fiberglass grating including yellow, gray, green and as your demands.
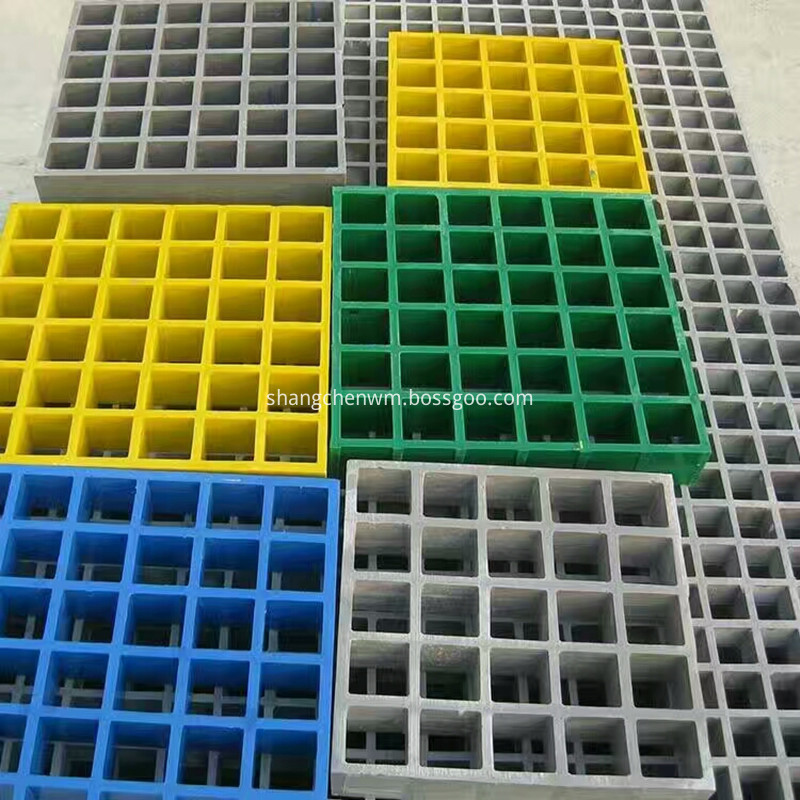
Fiberglass Grating,Fiberglass Dock Grating,Fiberglass Trench Grating,Frp Ceiling Grid Mesh
ANPING COUNTY SHANGCHEN WIREMESH PRODUCTS CO.,LTD , https://www.scwiremesh.com
